Unmistakable Warning Signs: How to Detect Hidden Electrical Dangers Before They Ignite
Electrical systems often whisper warnings before a catastrophe, and recognizing these quiet signals can prevent disaster. Start by paying attention to unusual warmth in outlets, switches, and cords, especially after prolonged use or high-power appliances. If a device or area feels hotter than normal, this is not just discomfort—it’s a red flag indicating potential overload or deteriorating insulation. Delays in trips from circuit breakers, or a breaker that repeatedly trips during routine use, suggest that the system is under stress and requires immediate inspection to avert overheating and possible ignition.
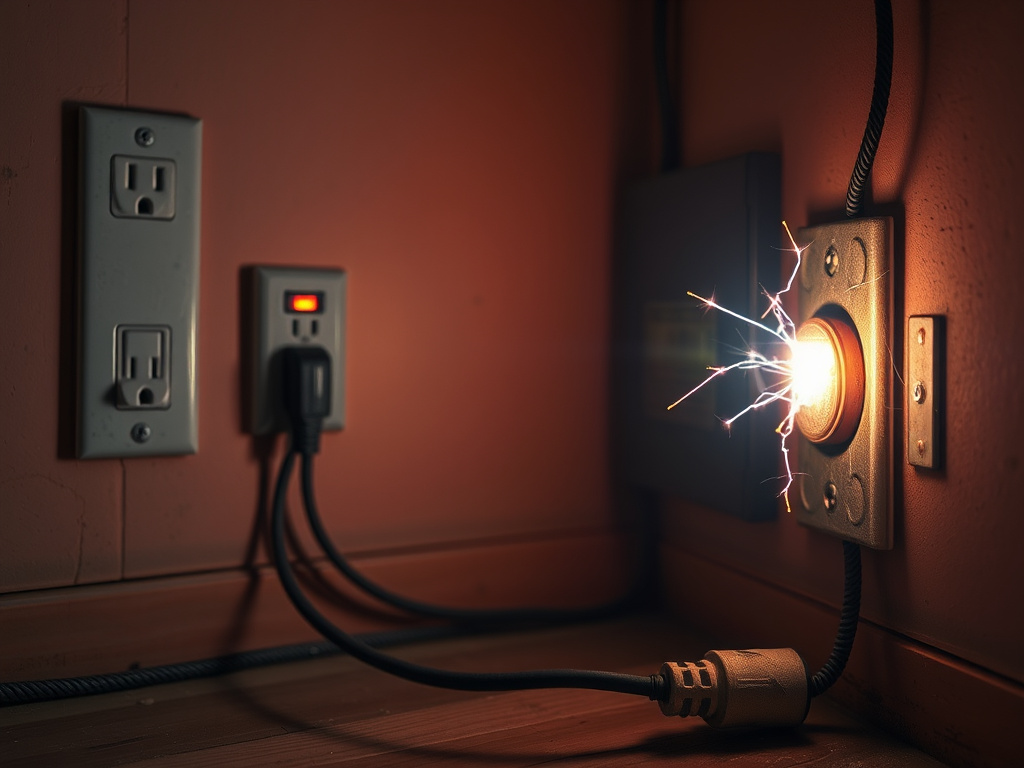

Sometimes danger announces itself through sounds and sight rather than sensation. Buzzing, crackling, or sizzling noises from outlets, switches, or light fixtures can signal loose connections, damaged cords, or arcing—conditions known to ignite flammable materials. Visible signs like scorch marks, discolored outlets, melted insulation, oruminous, flickering lights are not cosmetic issues; they point to compromised wiring that could spark a fire. Even faint, persistent smells of burning plastic or ozone indicate an urgent need for professional evaluation. Do not ignore these indicators, especially if they coincide with hot surfaces or frequent tripping of protective devices.
Creating a practical evaluation routine helps homeowners prioritize safety without becoming overwhelmed. Begin with a room-by-room inventory of outlets and cords, looking for frayed insulation, exposed wires, or overused power strips. Prioritize areas with moisture exposure, such as kitchens and bathrooms, where water and electricity pose amplified danger. Examine the condition of extension cords—never daisy-chain multiple cords or place them under rugs or heavy furniture. Consider the age of the electrical system; homes with older wiring may lack modern protections and require a full inspection. If any component shows signs of strain, replace it with certified equivalents and ensure that outlets have ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in appropriate areas to interrupt shock and reduce fire risk. For appliances, scrutinize cords and plugs for damage, avoid overloaded outlets, and never run cords behind walls or under furniture where heat can build up. Finally, maintain an ongoing plan: schedule professional electrical inspections at regular intervals, and keep a log of issues and fixes so that warning signs do not go unaddressed. This proactive approach transforms scattered observations into a coherent safety strategy that minimizes the chance of hidden faults becoming ignition sources.
The Heat Map of Your Home: Identifying Overloads, Faulty Wiring, and Hot Spots
Every room in a home has its own electrical fingerprint, and reading this fingerprint is essential to preventing fires. The heat map approach treats your house as a living network, where overloads, frayed insulation, and aging circuits leave telltale thermal traces that can escalate into dangerous situations if left unchecked. By learning to identify those hot spots, you empower yourself to intervene early, protect occupants, and reduce the odds of a catastrophic ignition.
In practical terms, you should begin with a broad sweep that combines both observation and measurement. Look for outlets and cords that feel warmer than the surrounding surfaces after normal use, especially in rooms with high electrical demand like living areas, entertainment centers, kitchens, and home offices. A gentle warmth might be a warning sign of an overloaded circuit or a poor connection; sustained heat, or heat that remains after devices are disconnected, points to insulation wear, loose terminals, or aging equipment that should be professionally evaluated. The goal is to map where heat concentrates so you can redistribute load, upgrade components, or install protective devices that curb risk before any flame or smoke appears.
The heat map concept also calls for an integrated approach to monitoring. Start by cataloging the daily power usage of devices with chargers, gaming rigs, heaters, or space heaters, and identify where multiple high-draw gadgets share a single outlet or power strip. If a single outlet feeds several high-load devices, that is a red flag that the circuit may be approaching its limit. In such cases, spread the load across additional outlets on separate circuits or install a properly rated surge protector and, where appropriate, a dedicated circuit for heavy appliances. This strategic distribution not only reduces overheating but also extends the life of your wiring and devices, creating a safer living environment.
Beyond the obvious heat signatures, you should also pay attention to the subtle temperature differentials that reveal hidden problems. Wires tucked behind furniture, in basements, or along baseboards may accumulate heat due to tight bends, damaged insulation, or degraded conductors. In kitchens and laundry rooms, where moisture and humidity accompany electrical use, indicators such as dampness on outlet faces, discoloration around sockets, or a persistent warm aura surrounding appliance cords should prompt an immediate inspection. Remember that heat does not always announce itself loudly; sometimes it whispers through a slow, creeping warmth at the plug end or within the wall plate. Treat these signals as urgent invites to check connections and circuit integrity before a fire risk escalates.
To turn this heat map into action, establish a practical monitoring routine that blends periodic professional assessments with routine homeowner checks. Use a non-contact infrared thermometer to scan outlets, switches, and switchplates in several key zones, particularly near windows, doors, and entryways where drafts can influence electrical load patterns. Keep a log of temperatures and any recently added devices or renovations—this historical data helps correlate heat spikes with specific changes in your home. If you notice persistent hot spots in areas serviced by old or ungrounded wiring, plan a targeted upgrade, opting for modern wiring standards, GFCI protection in wet areas, and proper cord management that prevents heat buildup. This proactive discipline transforms concern into clarity, allowing you to anticipate and neutralize hazards before they transition from heat to hazard.
Plugging the Gaps: Assessing Outlets, Cords, and Appliances to Prevent Fires
In the ongoing effort to safeguard homes from hidden electrical threats, the area around outlets, cords, and appliances demands vigilant scrutiny. Weaknesses here can masquerade as everyday wear and tear, yet they often act as the ignition points that escalate into fires. By adopting a methodical approach to inspecting these components, homeowners can intervene early, extend the life of devices, and reduce the risk of catastrophic outcomes. This section delves into how to evaluate outlets, cords, and appliances with clarity and practicality, drawing on concrete cues and proactive fixes that fit real-world living conditions.
Outlets and electrical devices form the frontline of safety in every room. Start with a systemic check of accessibility and condition: outlets that are recessed, loose, or cracked may indicate worn mounting hardware or internal loosening that compromises a secure connection. Gently testing plug-tightness can reveal outlets that have lost their grip, a condition that often leads to arcing or intermittent power delivery. If a plug wobbles or doesn’t sit flush, this is not mere aesthetics—it’s a warning sign. In kitchens and bathrooms, where moisture compounds danger, ensure that all receptacles in wet areas are GFCI-protected and rated for damp environments. It’s not just about compliance; it’s about ensuring that a single misplaced plug or a damp socket won’t turn a routine task into a fire incident.
Beyond physical integrity, the behavior of electrical devices offers invaluable clues. Appliances that hum, buzz, or exhibit delayed responses to plug-in actions suggest borderline connections or failing internal components. Discoloration around outlets, melted insulation on plugs, or a persistent, acrid smell of ozone or burning plastic should trigger immediate action—these are unmistakable signals that heat is accumulating where it shouldn’t. When such symptoms appear, consider unplugging the device and scheduling a professional evaluation rather than attempting do-it-yourself fixes that might worsen the problem.
Cord management is not merely about tidiness; it’s a critical safety measure. Overloaded power strips, extension cords running under rugs, or cords pinched behind furniture create hidden hotspots that can prematurely degrade insulation and ignite. A practical rule is to distribute high-draw devices across multiple outlets on separate circuits whenever possible, and to replace any cord with frayed insulation or damaged plugs. Never chain multiple extensions together, and avoid routing cords through doorways or under carpets where heat can accumulate unnoticed. In addition, ensure cords are compatible with the load they carry and replace damaged ones with UL-listed equivalents that match device amperage requirements.
When evaluating appliances, consider both the plug and the cord as critical components of a single system. Frayed cords or exposed conductors should never be repaired with tape or improvisation; instead, replace the entire cord or the unit if necessary. Appliances that run hot after use, struggle to start, or emit unusual noises may indicate motor or wiring issues that could spark a fire. Practically, establish a routine of unplugging and inspecting large or space-consuming devices after extended periods of operation, especially those with heating elements or motors. Maintain a habit of cleaning vents and filters to prevent overheating, and store cords in a way that avoids kinks and excessive bending at strain points.
To translate these observations into durable safety gains, recordkeeping becomes your ally. Maintain a simple log of outlet conditions, cord replacements, and appliance service dates, along with any noticeable changes in temperature or performance. This living history helps you identify patterns—such as a cluster of hot outlets in a single room or a cord that consistently heats up after a device is plugged in—so you can intervene with targeted upgrades, such as dedicated circuits, upgraded outlets, or more robust protective devices. In short, plugging the gaps requires a blend of careful inspection, prudent replacement, and proactive planning, turning routine checks into a robust shield against fire hazards.
Preventive Power Hygiene: Routine Inspections and Maintenance for Safe Circuits
Establishing a routine for electrical maintenance is the most reliable way to keep hidden faults from turning into dangerous fires. Preventive power hygiene means treating your home’s wiring like a living system that needs regular care, not a static backdrop for daily living. By integrating simple, repeatable checks into your week, month, and year, you can detect drift in performance, identify overheating trends, and address wear before it becomes a crisis. This approach reduces the guesswork and gives you concrete steps to extend the life of your circuits while protecting your household.
Start with a disciplined habit of documenting changes in load patterns. Note when certain outlets feel warmer than usual, when lighting fixtures flicker, or when appliances take longer to respond to a switch. These observations aren’t just quirks; they’re early signals that a circuit is nearing its capacity or that connections have degraded. Keeping a log helps you correlate symptoms with specific devices or rooms, making targeted interventions possible rather than reactive, last-minute repairs that can escalate risk.

Intertwined with observation is proactive habit formation around load distribution. Modern living often pushes home circuits to the limit with entertainment systems, charging hubs, and climate-control gear. A practical hygiene practice is to periodically rotate devices across outlets on different circuits to prevent chronic overloading on a single run. If you frequently notice heat buildup in one zone, that is not just a nuisance—it’s a cue to rework the layout, add a dedicated circuit, or install a higher-rated breaker where appropriate. This step-by-step adjustment reduces hot spots and keeps thermal stress within safe margins.
Maintenance also hinges on the quality and condition of components before problems intensify. Replace frayed cords, damaged plugs, and cracked outlets promptly with certified parts that meet or exceed current codes. Do not attempt improvised fixes that mask underlying faults; instead, adopt a policy of immediate replacement when insulation integrity is compromised or when a device exhibits abnormal overheating, buzzing, or discoloration around terminals. In parallel, schedule professional inspections at intervals suited to your home’s age and usage, ensuring that aging infrastructure is refreshed before aging becomes dangerous.
Incorporating preventive checks into daily life doesn’t have to be disruptive. The goal is to weave safety into routine household management—like quarterly thermostat and filter checks for comfort systems—and to elevate electrical care to a regular, expected practice. With a well-structured maintenance plan, you create a protective buffer that shields your family from the unpredictable risks hidden inside ordinary wires and sockets.
Finally, empower yourself with simple safety rules that translate into lasting protection. Always unplug high-draw devices when they’re not in use, especially in rooms prone to moisture or heat; keep outlets accessible and free from obstruction; and avoid daisy-chaining power strips or running cords beneath rugs. These practices, when consistently applied, act as the first line of defense against the silent drift that can quietly erode electrical safety and turn routine use into a dangerous scenario.
Smart Safeguards: Using Technology and Best Practices to Keep Electrical Systems Fire-Ready
Today’s homes are packed with connected devices, smart panels, and networked sensors that offer unprecedented visibility into how electricity flows through living spaces. Harnessing these tools effectively can turn potential fire hazards into manageable risk, turning spontaneous concerns into proactive protection. The core idea is to blend intelligent monitoring with proven safety practices so that even ordinary conversations with your electrical system become early-warning cues rather than emergencies waiting to happen.
Smart monitoring begins at the panel and extends to every outlet, cord, and appliance in use. Modern electrical systems often include motionless guardians such as smart circuit breakers, energy monitors, and device-level sensors that report unusual loads, rising temperatures, or arcing signatures. By enabling real-time alerts through a connected app, homeowners can spot divergent patterns—like a sudden surge when a television powers on, or a heater that drags a circuit toward its limit—before heat turns to hazard. Importantly, these systems can be configured to notify occupants when a circuit approaches capacity, when an outlet routinely runs warmer than its peers, or when a GFCI outlet trips without an obvious moisture source. This proactive feed of information shifts safety from reactive to anticipatory, giving families time to redistribute load, upgrade components, or schedule professional service without the pressure of an imminent fire event.
In practice, smart safeguards should be complemented by granular best practices that translate data into action. Start by establishing a centralized map of your household’s electrical footprint—identifying which outlets serve which rooms, which devices are on which circuits, and where heavy loads cluster. Pair this map with routine digital checks: review energy reports weekly, observe any device whose indicator light flickers or whose performance degrades, and set automatic reminders to test GFCI functionality quarterly. These steps do not replace hands-on inspection; they empower you to recognize patterns that previously required professional analysis and can now trigger timely interventions such as load redistribution, cord replacement, or the addition of dedicated circuits where needed.
Beyond consumer-grade sensors, the emergence of professional-grade diagnostic tools elevates your safety margin. Thermographic inspection cameras, once the domain of specialists, are increasingly accessible to homeowners as part of smart home packages or contractor-led services. Used responsibly, infrared imagery can expose subtle hotspots behind walls or within junction boxes, revealing concealed overloads long before they threaten insulation or trigger ignition. When combined with acoustic listening devices that detect faint arcing or loose connections, a diagnostic workflow emerges that is both precise and practical. The ultimate objective remains simple: transform hidden electrical strain into transparent, actionable information that guides upgrades and maintenance while keeping daily life uninterrupted.
Best practices also hinge on robust data hygiene and disciplined maintenance routines. Ensure that your smart devices are regularly updated with the latest firmware to close security and performance gaps that could compromise safety features. Maintain a clear inventory of all connected devices, noting which ones are high-draw or prone to overheating, so you can schedule preventative checks that align with device lifespans. Use only UL-listed, compatible accessories and avoid the temptation to consolidate loads onto a single smart hub or power strip. Finally, document every intervention, including the rationale for a circuit upgrade, the replacement of a damaged cord, or the relocation of a heater to a separate outlet. A well-kept history creates a reliable safety narrative you can reference during future renovations or when new devices are introduced to the home.